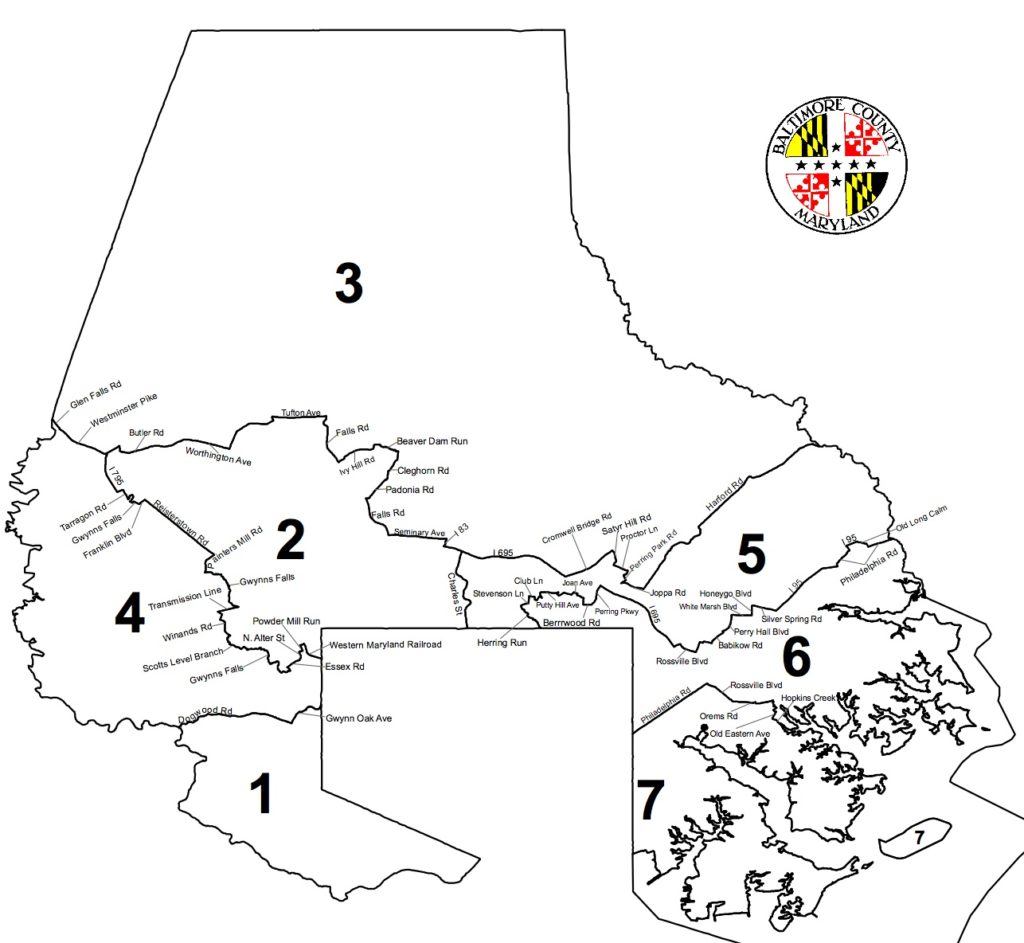
Baltimore County approved its new councilmanic district map on Monday. Here it is:
And here are the existing districts:
The ACLU of Maryland tweeted that it plans to file a lawsuit challenging the new plan under the Voting Rights Act (VRA). The Baltimore NAACP has already done so. Do they have a case? My educated guess is yes, though one would need to a more thorough analysis of the jurisdiction to be sure and to gather evidence needed for a successful VRA lawsuit.
The Supreme Court established a three-prong test in Thornburg v. Gingles (1986) that still sets the key conditions for proving a violation of Section 2 of the VRA.
First, plaintiffs need to prove that you could draw a “sufficiently large and geographically compact to constitute a majority in a single-member district.” The Baltimore Sun reports that map opponents have already shown that either the First or Second Districts, which are around 30% Black, could be converted into a Black majority district. The Fourth District is 72% Black; it could shed several predominantly Black communities and remain majority Black.
Second, plaintiffs must show that the minority group is “politically cohesive,” which just means that they need to show that Blacks in Baltimore County tend to vote together. This can usually be easily shown through analysis of election returns.
Third, and most crucially, plaintiffs must show that racial bloc voting usually defeats the minority group’s preferred candidate, usually referred to as a “candidate of choice.” Preferred candidates are those who win the vote in the Black community with candidates of the same race considered most probative evidence in a VRA lawsuit. However, non-Black candidates who defeat a Black candidate with the support of Black voters are also considered useful to examine for the purposes of a lawsuit.
In Baltimore County, no Black candidate has been elected to the Council except from the sole majority Black district. In the last state legislative elections, two Black state senators won in Baltimore County—both in majority Black districts. Four Black delegates also won election from majority Black districts. Excluding the district that is mostly in Howard County, the only Black Baltimore County state legislator who represents a non-Black majority district is Del. Carl Jackson but he was appointed in 2019, not elected.
Again, one would need to look more closely and further back to do a proper analysis, but all Black councilmembers and state legislators elected in 2018 won in Black majority districts (excluding Del. Terri Hill who represents the district predominantly in Howard).
In a lawsuit, Baltimore County might well argue that the new version of the First District is a second majority-minority district. In order to win on this basis, the defendants would need to show that the First District provides meaningful opportunity to elect the Black community’s preferred candidate. While it lacks a White majority, Whites form a strong plurality.
Even if plaintiffs win a VRA lawsuit, Baltimore County might not need to draw a second new Black majority district. Just because you need to show that you can draw a Black-majority district to bring a Section 2 lawsuit doesn’t mean that a new Black-majority district must be drawn to satisfy the VRA.
The standard is whether the district provides a meaningful opportunity to elect the minority’s preferred candidate. Since Black voters cast ballots disproportionately in the Democratic primary, they often comprise a majority of Democratic primary voters even when they do not in the voting-age population. This can allow a Black candidate to win the primary even without any White support.
If a Black candidate supported by the Black community can win the Democratic nomination in such a district, and the district is sufficiently Democratic that the nominee would win the general election, that district would still satisfy the VRA even though it is not a Black-majority district.
[Sidenote: If most Blacks voted for a Republican, then the Republican candidate would be the minority preferred candidate. I refer to the Democrats here because the reality is that the Democratic Party usually gets the great majority of the Black vote in Baltimore County and Maryland. But it’s all about the preferences of the voters.]
So why didn’t Baltimore County draw a second district that provides an opportunity for Black voters to elect their preferred candidate? That’s a story for another day.