Today, I am pleased to present a guest post by Dels. Marc Korman (D-16) and Erek Barron (D-24):
When we arrived in Annapolis in January of 2015, we immediately partnered to form the WMATA-Metro Work Group and bring more attention to issues related to Metro in Annapolis. After all, the state invests hundreds of millions of dollars to WMATA each year and increased oversight is sorely needed. We are cautiously optimistic that the new General Manager, Paul Wiedefeld, can bring some much needed change to WMATA. He has set out his own plan for reform, much of which we enthusiastically support. But after spending two legislative sessions hearing from WMATA officials and other stakeholders on an almost weekly basis, we have some of our own reform suggestions. Some of these are major structural or funding changes and others are more minor tweaks to Metro operations, but we think all are worthy of discussion by WMATA and the region.
Out the outset, we should note that none of these ideas can replace or should distract from the immediate safety work necessary for the system to operate. SafeTrack and other efforts are important, but it is our hope that some of these ideas can keep the system from finding itself in a situation like the one it is in now ever again.
Board
Board Structure: The WMATA Board is the primary means of providing oversight of Metro. But each appointing jurisdiction treats the Board in a different fashion. In Maryland, Board members are Gubernatorial appointees and answer to the Governor. In the District of Columbia, usually a Councilmember and a Mayoral appointee serve as the Board Members. In Virginia, there is a divide between state and local appointees. The District and Virginia have elected officials on the Board, while Maryland and the federal government do not. The Board members all receive different levels of pay from their jurisdictions. This structural mismatch causes disharmony on the Board, makes Board members’ different perspectives even more pronounced, and is generally inefficient. Standardizing how each jurisdiction treats the Board so that their appointees are similarly positioned would improve the Board’s critical governance function.
Resources for Board Members: The WMATA Board is a strange beast. It is the primary method of oversight for WMATA, yet its Board Members essentially have no resources. Board members who are elected officials or work in government may be able to use those resources to support their work, but other members do not have those options. Consideration should be given to providing board members with the resources and ability to provide adequate oversight and independent analysis of WMATA activities, instead of being forced to rely entirely on WMATA staff.
Board Meeting Options: WMATA board meetings seem to follow a basic pattern in which WMATA staff tells the Board what they want to do on an issue, the Board asks a few questions, and the item is usually agreed to. Sometimes, the Board pushes back and the staff has to withdraw the item and come up with alternatives at a future meeting. Staff should consider providing more options up front for the Board on major issues (such as fare options) and let the Board make more informed decisions on the basis of those options.
Public Meetings and Access: WMATA Board Members have made an effort over the last year or two to show up at stations and meet with riders. Far more of this public engagement and outreach is necessary. Whether that is stepped up station visits, rider-focused town halls, or better use of social media, WMATA needs to engage its riders. Twitter, for example, is not a random sampling of riders, but the frustration expressed in the Twitterverse is palpable and more opportunities need to be created to allow riders to express their concerns to WMATA board members and personnel.
Auction Board Seats: Someone in Annapolis suggested this idea to us. If jurisdictions want more say over how WMATA operates, they could compete for additional Board seats—with an overall cap—through an auction process: a Board seat could be bought in exchange for additional operating or capital subsidies. This could provide WMATA with necessary additional revenue.
Secretarial Board: An entirely different Board model has been floated by a WMATA board member, which would be to have a more focused Board made up of the Transportation Secretaries—or an Assistant Secretary—from each jurisdiction. It would be a radical change from the current model, but might make WMATA more politically accountable by tying the Board more directly to the elected leadership in each jurisdiction. There are issues with this approach, such as how to handle Virginia’s localities, but this is a radical reform that should be discussed. If this radical reform is a bridge too far, then perhaps an “Executive Council” of each jurisdiction’s transportation secretaries could meet on a regular and scheduled basis to address major issues, providing guidance to the Board as to what will be acceptable to the compact members.
Funding
Dedicated funding: Probably the number one suggestion people have about WMATA is a dedicated funding source. Currently, only Northern Virginia has any “dedicated funding” for WMATA, with a 2% gas tax being allocated to WMATA and making up less than 15% of the entire Virginia operating subsidy. Meanwhile, the District of Columbia actually passed legislation in 2006 dedicating one half of one percent of its retail sales tax to WMATA, but it was contingent on similar action by the other jurisdictions which never occurred (it was estimated that this would raise $50 million) at the time. Dedicated funding would not be a cure all for Metro’s woes, but would definitely help. Options for dedicated funding include a regional sales tax, transfer tax, a property tax supplement for property near Metro, and several other options. Although progress on this issue continues to lag, it should remain a part of the conversation. Board Chairman Jack Evans has made it front and center to his agenda, although any funding change should come with governance and management reforms.
Federal Operating Subsidy: All of the Compact jurisdictions, except the federal government, provide an operating subsidy to Metro. Indeed, the federal government was given Board seats in exchange for a non-guaranteed annual capital appropriation of $150 million. The federal government should also provide an annual operating subsidy to WMATA, just as other jurisdictions with Board seats do. This should become a top priority for our region’s Congressional leaders. Again, Board Chairman Evans has rightfully been discussing this issue.
Stations
Station Ownership: Station Managers need to take more ownership of their stations. The new GM’s plan includes establishing management ownership of each rail line to improve the customer experience and something similar should occur with the Metro stations. Some Station Managers do stand outside of the control booth and take pride in their stations, bar far too many are inaccessible in the control booth and unaware of what is happening in the station, not making sure it is welcoming, clean, and functioning. Station Managers should be appropriately compensated and incentivized to take more ownership of their stations.
Station Task Forces: In one of our districts, a group of local residents, businesses, and government leaders formed a station improvement task force to try and improve the Bethesda Metro Station. Their efforts have improved cleanliness at the station, brought in new public art, and put Bethesda at the forefront of station modernization efforts. This model should be followed at every station in the system to make sure every community is getting the attention and improvements it deserves.
Escalator Alignment: Most stations have a standard traffic flow to them. Those in downtown DC have more exiting passengers than entering passengers in the morning and vice versa in the suburbs. Yet escalators are not regularly adjusted for this natural schedule. If a station has three escalators, two of the escalators should be aligned in the direction of the most travel and that should be switched at the appropriate time during the day by Station Managers. This will reduce crowding and be generally more convenient for riders.
Vendors: Even with declining ridership, thousands of people stream in and out of rail stations and major bus stations on a daily basis. WMATA needs to focus more on revenue capture from these opportunities, such as shoeshine stands, coffee shops for those exiting, or even small pharmacy stands. WMATA needs to get aggressive about alternative revenue options besides fares and jurisdiction subsidies.
Signage: Metro stations are hard to navigate, particularly for tourists. Those unfamiliar with where they are try to squint through grimy windows into dark stations with signs few and far between. Someday, when all the railcars are new, station announcements will be clear and in-car displays will explain what station the train is at. But there is no need to wait to add additional signage throughout Metro stations.
Metro Aesthetic: Metro stations were built as cathedrals with high ceilings, dim lighting, and an expansive feel. Unfortunately, the large stations are hard to heat and cool, the lighting fixtures and walls are difficult to clean, and the darkness raises safety issues and is inconvenient for passengers waiting for single tracking trains while trying to read. Yet many traditionalists want to maintain this “Metro aesthetic” as though the system were new. We cannot be bound to the design decisions of decades ago. Some stations can be preserved for historical reasons, but most should be updated and modernized when funding is available with better signage, lighting, and less “Metro brown.”
Maintenance
Easy Infrastructure: Within the past few years, an additional stairwell between the platform and Mezzanine was added at the Bethesda Metro station. This low cost and easy infrastructure improvement has eased escalator crowding and spread people out at the station. Additional easy infrastructure changes should be quickly evaluated and undertaken as they are low cost but high reward.
Repeat Work: There is a concerning pattern with WMATA needing to repeat maintenance work multiple times. A recent example of this was the inspection of the jumper cables on the day of the shutdown. These cables had supposedly been inspected after the L’Enfant Plaza incident, but somehow major problems were missed. We are also on the third attempt at sustainable escalator repairs: We began with spot fixes; WMATA then tried to take apart, clean, and rebuild the escalators; and now we are on full replacement. Recent discussion of the need to potentially close entire lines for more maintenance—after years of a capital program that has been extremely disruptive—may be the latest example of the necessity for repeat work. How much other work is being done multiple times? WMATA needs to quickly get to the bottom of this problem.
Single Tracking: One of the major frustrations with Metro’s rebuilding efforts is the single tracking and long delays. Indeed, the system is virtually un-rideable on the weekends. But many transit systems operate on only two tracks. New York is actually unique in the amount of track redundancy it has built in. WMATA should canvass other transit systems to make sure it is using modern best practices when it comes to serving its customers safely while doing necessary rebuilding.
Fares
Low Income Fares: The maximum WMATA rail fare is a whopping $5.90, compared to a flat cost of $2.75 in New York City or $2.50 in Atlanta. Because of that high cost, many low income riders cannot use the system. Some jurisdictions, such as Boston, are experimenting with lower fares for low income riders. WMATA should follow suit.
SmarTrip on MARC: Baltimore City and WMATA have an interoperable SmarTrip card. But the transit option that connects them—the MARC train—does not accept SmarTrip. WMATA should work with the Maryland Transit Administration to change this and truly connect these two urban centers. We are biased towards Maryland, but if Virginia wants to pursue something similar on the VRE, that should be supported as well.
Safety
Safety Culture: Safety culture is discussed a lot in reference to WMATA. Supposedly, a safety culture was established after the Fort Totten incident but ongoing events suggest otherwise. The new General Manager seems to have really changed the tone at WMATA. One of the issues we have observed is that the “safety culture” at WMATA often boils down to checking off NTSB or FTA safety recommendations and directives. But a safety culture is not just checking boxes to rectify previously identified problems. It requires all WMATA personnel to be looking over the horizon for other safety issues and concerns. That is the attitude WMATA management needs to demand and implement.
Rail Operations Control Center: Reports about the Rail Operations Control Center (“ROCC”) are incredibly concerning. WMATA claims it has new employees in training to re-staff the ROCC, which is currently understaffed. But there are reports that the current staff at the ROCC push new people out to protect their overtime. This obviously needs to be seriously addressed. One idea is to raise the base pay of those in the ROCC and bring on more, trained people quickly. Some may view such a move as rewarding bad behavior, but something has to be done quickly to improve the climate at the ROCC and its contribution to a safe system.
Bus Mirrors: Many of the safety issues currently discussed relate to rail, but there are bus issues as well. One issue raised by bus drivers is that the side rear view mirrors block sight lines and endanger pedestrians who drivers cannot see. This has been the subject of litigation in other jurisdictions and there are simple solutions to reduce the size of mirrors and improve safety.
Automatic train control (“ATC”)
Metrorail has operated largely without automatic train control since the 2009 Red Line collision. Last spring, ATC was restored for eight car Red Line trains, but six car trains and trains on the system’s other lines remain in manual control. Restoring ATC system-wide is crucial for both safety and reliability. Currently, it is not uncommon for train operators to have to move their train a few additional feet forward to meet the end of the platform after stopping at the station. This creates a jerky experience for riders as they prepare to exit the train, since most don’t expect the train to move again once it’s already stopped. Less frequent but far more inconvenient are instances where a train operator overshoots the platform and must skip the station altogether. Returning to ATC will eliminate these problems while increasing safety and reliability. While restoring ATC and ensuring that it functions safely is a large and complex task, it must remain a priority in order to make the system safe and convenient.
Riders Advisory Council (“RAC”)
RAC Selection: Metro’s RAC has six members each from Maryland, Virginia, and DC, two at-large members and the head of the Accessibility Advisory Committee. Members are appointed by the WMATA Board. An alternative approach that would improve RAC independence would be to have the RAC appointed by the heads of the state or local governments in the WMATA Compact. That would ensure that the RAC is truly independent of the Board and representing the riders.
RAC Jurisdictions: RAC’s members in Maryland and Virginia are all from the local jurisdictions that make up the Washington Metropolitan Area Transit Zone (Arlington, Fairfax, Loudon, Alexandria, Falls Church, Montgomery, and Prince George’s). But there are many riders from other nearby counties such as Frederick or Prince Williams. The option should be available to have RAC members, perhaps the at-large members, from these other jurisdictions.
Miscellaneous
Benchmarking: One Montgomery County Councilmember has called for benchmarking WMATA to peer systems. This type of public benchmarking would be helpful and is already in use by some systems. Every system is different, but it would be useful to see how WMATA compares to peers on some key indicators such as on-time performance, car utilization, and so on. Community of Metros (“CoMET”) is already doing this type of work and WMATA should join the effort.
Ride Sharing: There has been concern expressed recently about ride sharing’s effect on transit and whether ride sharing can be adequately used for paratransit. WMATA should begin pilot programs to use ride sharing to connect some riders’ last mile connections to bus and rail transit. Usually, riders need to be less than a half mile from transit to regularly access it on foot. Ride sharing can expand that envelope.
Archives/Documents Office: WMATA no longer has an official in charge of preserving and making publicly available historic documents. This reduces public accountability for WMATA’s actions. If you have ever read Zachary Schrag’s The Great Society Subway, an incredible account of WMATA’s history, you know the insight that can be provided by making historical material available.
Ridership Reports: Last year, Maryland passed legislation requiring a Maryland-specific ridership report from WMATA. Most of the data is already collected by WMATA, but this required a jurisdiction-specific report to demonstrate how WMATA is used, especially by those outside of the Montgomery and Prince George’s County. Ridership from other counties outside the compact helps justify the substantial expense Maryland rightly pays for WMATA. Ridership reports that similarly track DC, Virginia, and even federal employee and contractor ridership would go a long way to demonstrating in detail the benefits of the system.
Jurisdiction Work Groups: WMATA oversight is complicated because of its multi-jurisdictional nature. When we were elected, we formed a work group in Annapolis to try and provide some oversight to the system. Indeed, almost every week during our legislative session we are joined by a WMATA staff member or other stakeholder to discuss in detail some of the issues, challenges, and opportunities before Metro. We believe this is a useful model that the other jurisdictions should follow. Oversight by the jurisdictions tends to come after emergencies, but real oversight is regularly occurring and not just reactive.
Reduce Turnover: WMATA has a surprisingly high turnover rate. Between 2009 and 2013, 417 of 535 train operators turned over. Considering that these are well compensated union jobs, that is a high turnover rate. Reducing that turnover rate for train operators and other positions will allowed better trained and experienced personnel to operate the system. That does not mean WMATA should retain personnel not acting appropriately, but turnover should not be systematically high.
Real Estate Coordination: WMATA has a robust real estate development operation as it tries to improve transit-oriented development on land it owns around stations. That office could improve in two ways. First, much more communication and coordination is needed with local elected officials who represent the areas around the stations and with the local business community and residents. These stakeholders have little insight from WMATA on their plans. Second, the real estate office is solely focused on WMATA’s holdings. But it has great expertise in transit-oriented development that it could offer to other landowners around stations to make sure that we are meeting our economic development goals around Metro. Another outside the box idea being floated is to spin-off this function from WMATA entirely, which is certainly an idea worth considering.
Parking: WMATA operates 44 parking facilities at Metrorail stations. This means that in addition to all of its other functions, WMATA is also managing a whole other line of business, parking. WMATA needs to consider whether the parking business should be subcontracted or even spun off into another public entity to better manage its operations.
Metro Innovation: Another unfortunate trend we have noticed during our Work Group meetings is a status quo culture: WMATA personnel’s insistence that everything is going according to plan. WMATA rarely admits errors or mistakes and often gives the impression that if they were just left alone by the public and the press, everything would be fine. This status quo attitude is obviously not shared by the new GM, but that is another cultural issue that needs to be addressed at the agency. To change this culture WMATA should encourage its leadership teams to select system challenges and, following the path of the tech industry, think of new approaches to bring value to WMATA and its customers. One area ripe for innovation is Metro Access, the paratransit service. This service is costly and causes frustration for many users. Innovation in Metro Access is absolutely necessary whether it is more pilot projects for certain populations as currently exists in Montgomery and Prince George’s County where regular, dedicated drivers are being used for certain groups; better GPS technology for routing; or even ride sharing with adequate protections where appropriate.
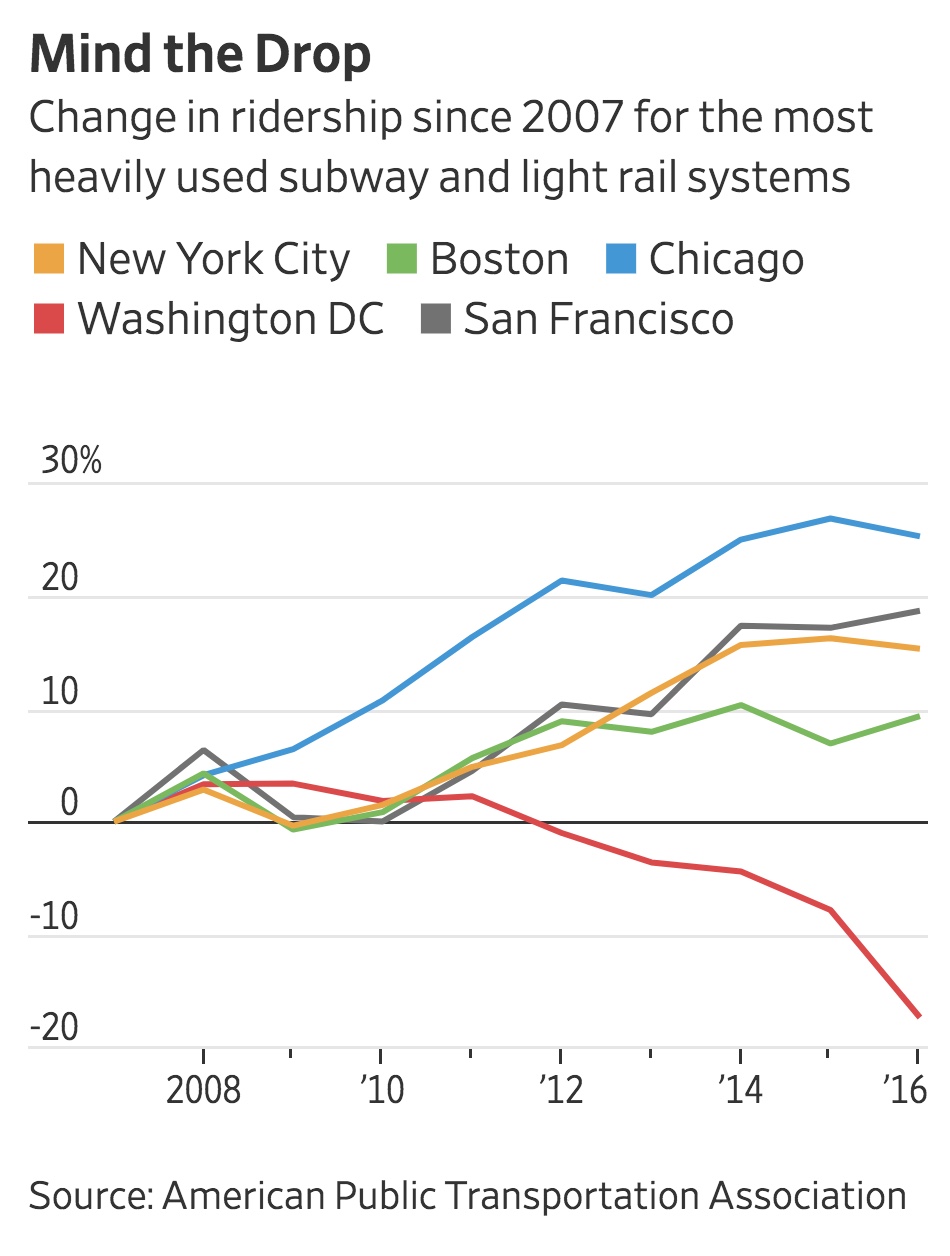 One of the responses to Metro’s critics is a variation of “things are tough all over.” Not so fast. Other major subway and light-rail systems may have problems but this graph from yesterday’s Wall St. Journal shows that WMATA is in a class all its own. Ridership is down 19% from 2011 through 2016. And no one thinks those figures are picking up even though SafeTrack is over and we’re theoretically “Back to Good.”
One of the responses to Metro’s critics is a variation of “things are tough all over.” Not so fast. Other major subway and light-rail systems may have problems but this graph from yesterday’s Wall St. Journal shows that WMATA is in a class all its own. Ridership is down 19% from 2011 through 2016. And no one thinks those figures are picking up even though SafeTrack is over and we’re theoretically “Back to Good.”