By Adam Pagnucco.
Last fall, County Executive Ike Leggett proposed cutting the volume of new general obligation bonds issued by the county in future years and the County Council concurred unanimously. Advocates for school construction fretted over the move as the county’s needs in that area, as well as in transportation investment, are enormous. But Leggett and the council had a point. The county’s debt has skyrocketed in the past twenty years and especially in the last decade. It now presents a substantial challenge to the county’s fiscal well-being that the next generation of county leaders will have to deal with.
The county government does not use debt to finance its operating budget, but it does use debt to finance its capital budget, known as the Capital Improvements Program (CIP). The CIP is a six-year budget that is fully renewed every two years and is adjusted in off years. The Executive’s latest recommended CIP currently totals $4.5 billion, of which $1.8 billion is recommended for school construction. The CIP has many funding streams for its projects, but the single largest one is debt. As of June 30, 2017, the county had $4.1 billion of outstanding primary government debt, of which the largest category is general obligation (GO) bonds, which accounts for $2.7 billion. GO bonds are backed by the full faith and credit of county government. The fact that the county’s GO bonds have had a AAA rating assigned to them by the nation’s three largest credit agencies for many years is a substantial source of interest savings to the county. Other major categories of debt are short-term bond anticipation notes ($500 million outstanding), taxable Build America Bonds created during the recession ($308 million) and revenue bonds which are backed by dedicated revenue streams ($222 million). All of this is separate from the substantial liabilities the county has for pension funding and retiree health benefits.
There are two salient facts about the county’s debt. First, it has been growing rapidly. And second, it is paid off through debt service that is part of the county’s operating budget. These debt service payments MUST be paid and they compete with other spending priorities. Along with total debt, debt service has also been growing rapidly.
The chart below shows growth in total outstanding primary government debt and in GO bonds over the last twenty years. While growth has occurred throughout the entire period, it has accelerated since the onset of the Great Recession. From 1998 through 2008, GO bond debt grew by an average of 2.9% per year, about equal to growth in the Washington-Baltimore CPI (3.0% per year). Total debt grew by an average of 5.2% annually over that period. From 2009 through 2017, GO bond debt grew by an annual average of 8.1%. Total debt grew by 8.4% annually. The average rate of inflation in the Washington-Baltimore CPI was 1.5%. Over the last eight years, the county’s debt has been growing by more than 5 times the rate of inflation.
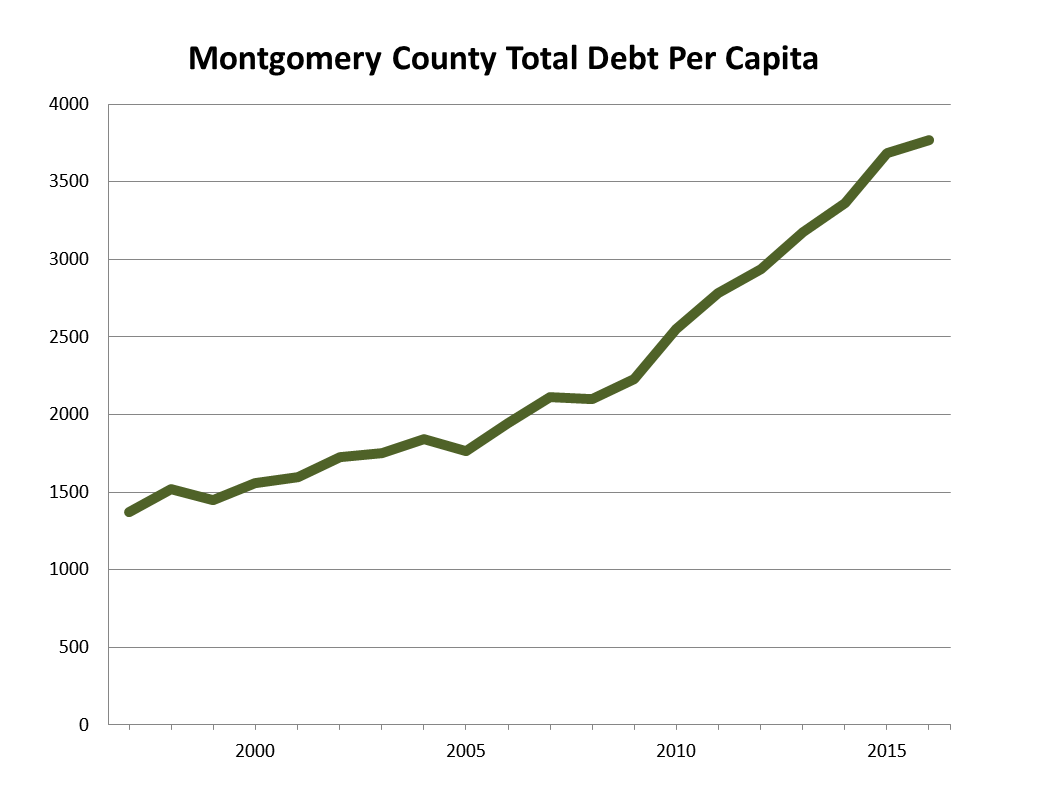
Relative to the size of the population, the debt has been rising too. When we compared the county’s total debt levels to population estimates from the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, we found that total debt per capita has grown from $1,370 in 1997 to $3,768 in 2017.
As for debt service, it has risen from $140 million in FY97 to $408 million in FY18. If debt service was a county agency, it would be the largest agency in county government other than MCPS. Debt service payments are mandatory and cannot be cut like most other categories of spending during recessions. The pit of the Great Recession came in FY11, when debt service was $258 million and the county slashed services, doubled the energy tax and furloughed its workforce. Now that debt service exceeds $400 million a year, it will present a much greater impediment to the maintenance of county services when the next recession comes.
Let’s remember that debt is not an inherently bad thing. It is the primary vehicle by which the county pays for core government functions like school construction and transportation projects. The county’s needs in those areas are absolutely undeniable. Also, construction costs were moderated during the recession, so the county was able to take advantage of that to build relatively cheaply in those years. But over the long term, if you are going to have rapidly growing debt, you need to have a rapidly growing economy to pay for it. And MoCo does not have that – instead, it has had weak growth in employment and incomes in recent years. It saw 57 new business filings in 2015 and 19 new filings a year later. It passed a 9% property tax hike and a year and a half later suffered a $120 million budget shortfall.
This is evidence yet again that an economic revival has to be a huge priority for the next generation of county elected officials. Without it, debt service will consume larger and larger chunks of the budget and eventually lead to service cuts and/or tax hikes. As for those who oppose economic growth or have worked to undermine it, the debt situation makes this clear: you cannot oppose growth and favor expanding school construction and transportation investment. The economy and the credit markets won’t allow elected leaders to have it both ways.
Bear that in mind as we head to Election Day.