By Adam Pagnucco.
On Friday, County Executive Marc Elrich issued the first veto of his administration against a bill by the county council offering 15-year property tax breaks for high-rise developments at Metro stations.
Vetoes are uncommon events in MoCo politics. Elrich’s predecessor, Ike Leggett, vetoed three measures: a county property disposition bill in 2012 (which was overridden), a minimum wage bill in 2017 (which was subsequently replaced by a similar bill that he signed) and a 2018 line item in the capital budget covering stormwater contracting (which resulted in passage of a compromise). Vetoes are typically prevented by one of two things: deal-making between the executive and the council or passage of a measure by more than the six votes required to override. But there was no deal in this case: Elrich opposes the property tax bill and wrote his rationale in a lengthy veto message.
This post examines the policy debate around the bill, about which I wrote a three-part series. (Here are links to Part One, Part Two and Part Three.) Tomorrow, we will discuss the politics.
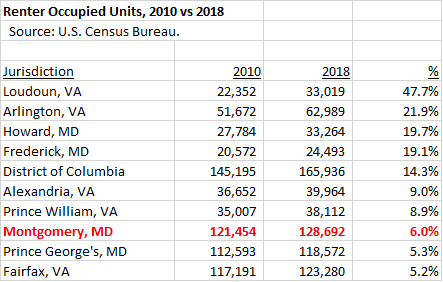
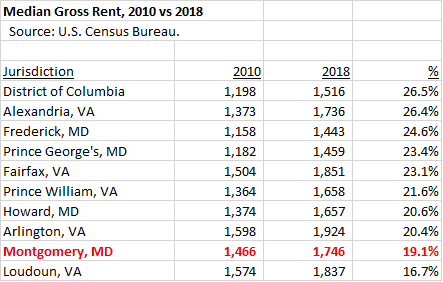
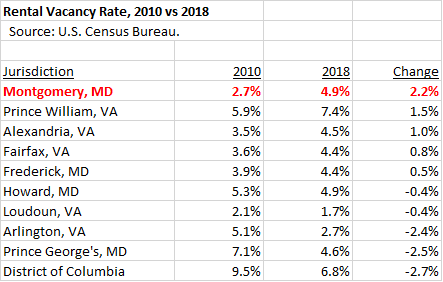
Bill 29-20, the target of Elrich’s veto, originated from three related events. First, Montgomery County, like the rest of the region, has a shortage of housing when compared to projections of population growth. This was chronicled in a report by the Metropolitan Washington Council of Governments (MWCOG), resulting in passage of a resolution by the county council to meet the county’s share of regional housing growth. (Elrich was notably skeptical of this.) Second, for at least the past fifteen years, the county has chosen to concentrate new density around Metro stations through its master plans for a combination of reasons related to transportation, environmental concerns, placemaking and preservation of the Agricultural Reserve. (Elrich voted against many of these master plans when he was on the council.) Third, Fivesquares Development, which was selected by WMATA as its ground lease development partner at the Grosvenor-Strathmore Metro Station, has proposed a housing development including high rises at the station. However, Fivesquares has since said that the economics of the site won’t allow anything more than low density development unless they obtain a subsidy.
These events gave rise to Bill 29-20, which offers developers at Metro stations 15-year property tax breaks if they build high rises. The bill’s supporters claim that without the tax breaks, the sites will either remain undeveloped or will contain low- or mid-rise projects that waste the stations’ potential for generating transit-oriented development. Elrich disagrees, offering several key reasons that I will evaluate.
Elrich: The bill “harms the budget.”
Elrich wrote:
At a time when the County is struggling to fund critical services, where the outlook for the next couple of years is uncertain at best, and where full economic recovery from this pandemic may take as much as ten years, it is certainly not prudent to reduce revenues coming into the County coffers.
The bill’s supporters argue that the tax break would only apply to projects that would otherwise not happen without the bill, thus not creating a real marginal cost to the county. They also say that without the bill, the Metro stations would remain undeveloped and therefore pay nothing to the county. However, according to Fivesquares, a low density project would be viable at Grosvenor-Strathmore without a subsidy and would therefore generate actual property taxes for the county. So even without the bill, it’s possible to get taxpaying low- or mid-rise development at Metro stations. The real question is not so much about the budget but whether the public benefit of high-rise housing infrastructure at Metro stations is worth an investment of public dollars. Elrich says no, the bill’s supporters say yes.
Elrich: The public benefit isn’t worth it.
Right now, developments at Metro stations are required to ensure that 12.5-15% of constructed units are moderately priced dwelling units affordable to moderate income people. Council Member Will Jawando amended the bill to require that 25% of a qualifying project’s units be moderately priced to get the tax break. Elrich says there should be a higher percentage of moderately priced units and he argues that they should be mandated rather than included in a tax incentive. (If he believes that, he should send over legislation to accomplish it.) Bill supporters argue that a higher percentage of affordable units would kill a project’s economics. The record of the bill does not conclusively prove either side right.
Elrich: Public funds should be used for affordable housing, not market rate housing.
Elrich argues that MoCo’s real housing shortage is in affordable units, not so much in market rate units, and that because the bill allows projects with 75% market rate units to get tax breaks, it contributes little to solving the county’s housing problems. He is right that MWCOG’s report recommends that “at least 75% of new housing should be affordable to low- and middle- income households.” But with all due respect to MWCOG, the difference between the county’s requirement that 12.5-15% of new units be moderately priced and the report’s recommendation that 75% of them be affordable is VAST. The county’s housing target is 10,000 units above forecasts. No one – not Elrich, not the council, not the planning board – has a credible financing plan for plowing (at least) hundreds of millions of dollars of public money into building 7,500 or more affordable units. Holding this bill or any other plan to that standard is unrealistic.
Elrich: The bill sets a difficult precedent.
Here, Elrich makes the same slippery slope argument that I made. If developers at Metro stations get these tax breaks, developers of properties next to Metro stations will want them too. The bill’s supporters argue that Metro sites have extra costs that require subsidies to offset. Those extra costs are probably responsible for the dearth of new high-rise projects at Metro stations all around the region. But the bill does change how the county does incentives. In the past, incentives have been granted on a case-by-case basis (including the Marriott headquarters development project). The bill establishes its subsidy in law, giving it to developers by right. The bill’s supporters don’t say this publicly, but they argue privately that legislation is necessary because Elrich can’t be trusted to constructively negotiate with developers. Even if that were true, Elrich won’t be executive forever, and case-by-case negotiations have advantages that a one-size-fits-all approach can’t replicate.
Elrich: Construction workers deserve prevailing wages.
Council Member Will Jawando offered an amendment to require that Metro station development projects should pay construction workers the same prevailing wage they receive on county construction projects to get tax breaks. The amendment failed on a 4-5 vote, with Jawando and Council Members Evan Glass, Tom Hucker and Sidney Katz voting in favor. Elrich cites the bill’s failure to require prevailing wage as a reason to veto it.
When I was employed by the carpenters union, I lobbied the council to pass what is now the county’s prevailing wage law. In doing so, I provided them with a mountain of evidence that prevailing wage laws do not inflate construction costs because higher wages tend to be offset by higher productivity. As Nooshin Mahalia of the Economic Policy Institute wrote just before the bill was passed:
An overwhelming preponderance of the literature shows that prevailing wage regulations have no effect one way or the other on the cost to government of contracted public works projects. And as studies of the question become more and more sophisticated, this finding becomes stronger, and is reinforced with evidence that prevailing wage laws also help to reduce occupational injuries and fatalities, increase the pool of skilled construction workers, and actually enhance state tax revenues.
Council Member Marc Elrich was a co-sponsor of the prevailing wage bill. No current council member was in office when it passed in 2008.
The county has a prevailing wage law for its construction projects. WMATA uses the federal prevailing wage law (the Davis-Bacon Act) for its construction projects. And yet a developer with a county subsidy building at a WMATA Metro station is not required to pay prevailing wage. That just does not make a lot of sense.
Those who voted against prevailing wage coverage argue (against the evidence linked above) that it would inflate project costs and offset the value of the 15-year property tax break. If they truly believe that prevailing wages increase costs, then to be intellectually honest, they should repeal the county’s prevailing wage law to save money for the capital budget. Unless they do that, the arguments against prevailing wage ring hollow. On this one, Elrich is right.
The best point that Elrich’s critics make against him is that if he opposes this bill, then what is his plan to build more affordable housing? The county’s current total of $62 million in operating and capital money for preserving and building affordable units is woefully inadequate when compared to the needs. Elrich has been discussing this issue while in elected office for 14 years. What is the Elrich Plan to Build Affordable Housing?
Tomorrow, we will get into the politics of the veto.